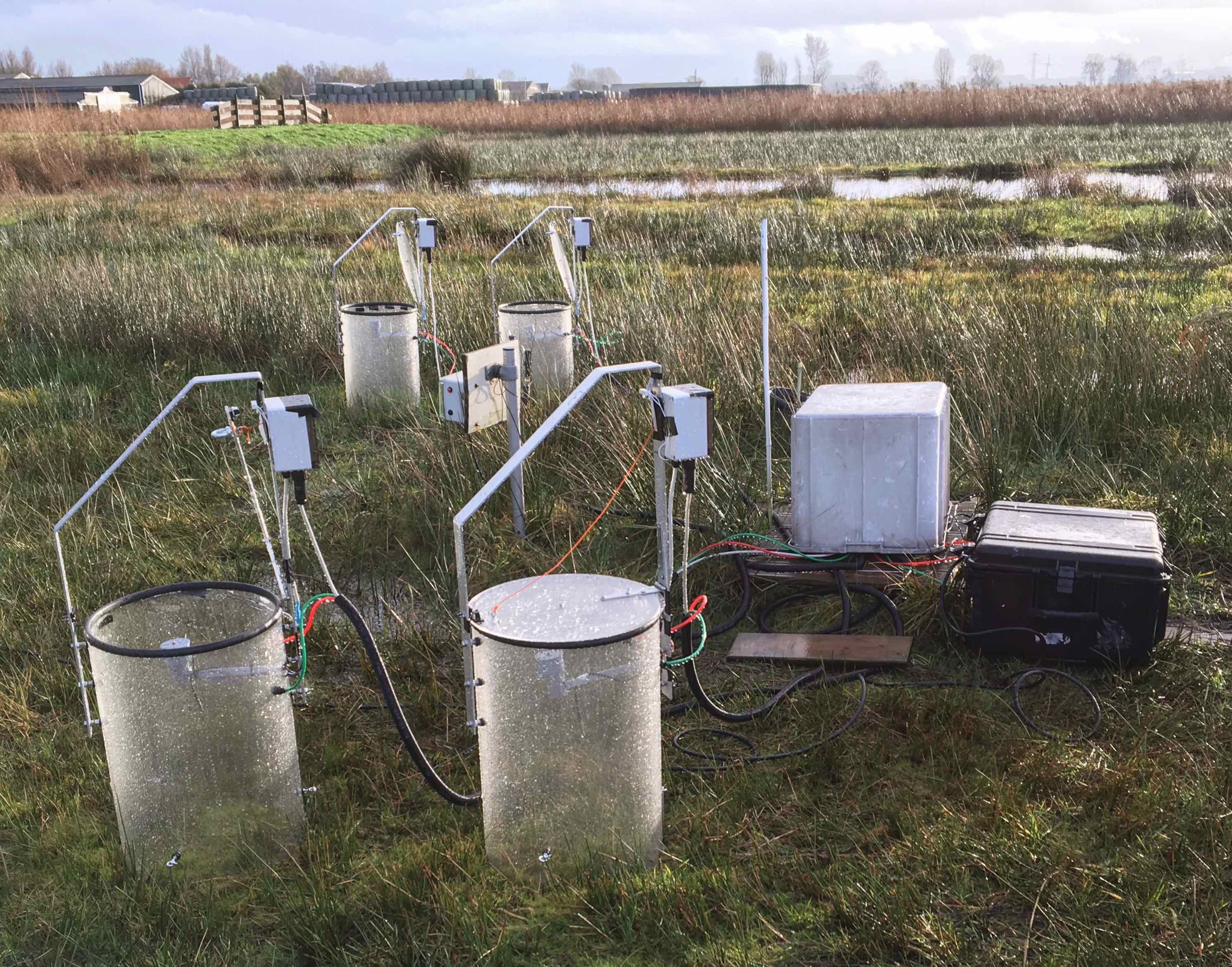
 Now in operation: automatic static chamber system for measurements of gas fluxes from soil and vegetation (carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide).
Now in operation: automatic static chamber system for measurements of gas fluxes from soil and vegetation (carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide).
This system is based on many years of experience with measurements of greenhouse gas uptake and emission from soils. It has been extensively tested in various locations and weather conditions.
The system consists of four chambers (more is possible). If the lid of the chamber closes, the measurement starts; the flux equals the gas concentration increase rate in the chamber. The closing time of the chambers can be adjusted in a simple manner.
This chamber system can be connected to any gas analyzer that transfers its data via a serial port or ethernet connection.
The chambers are controlled by a microcomputer, that also stores the data of the gas analyzer. Additional sensors include a barometer, air and soil temperature sensors. Diverse configurations of the chambers (transparant or opaque) are optional. Power usage of the system amounts 55 W (excluding gas analyzer).
Measurments with an automatic chamber system are considerably cheaper than those using eddy covariance systems and may be appied on smaller test locations.
Methane scanner
The methane scanner consists of a microcomputer with a GPS system, coupled to a mobile gasanalyzer. The system can be configured for several types of gasanalyzers.
In this way methane sources can be mapped rapidly and at a large scale, including possible natural gas leaks and emission sources from agriculture. The picture to the right shows results. It represents a part of the city of Amsterdam; the vertical bars show positive deviations from the methane concentration from the average. One big source (lower part of image) may have been methane released from peat soil exposed in a construction pit, the other large source area (upper part) may consist of gas leaks and methane from canals in the older parts of town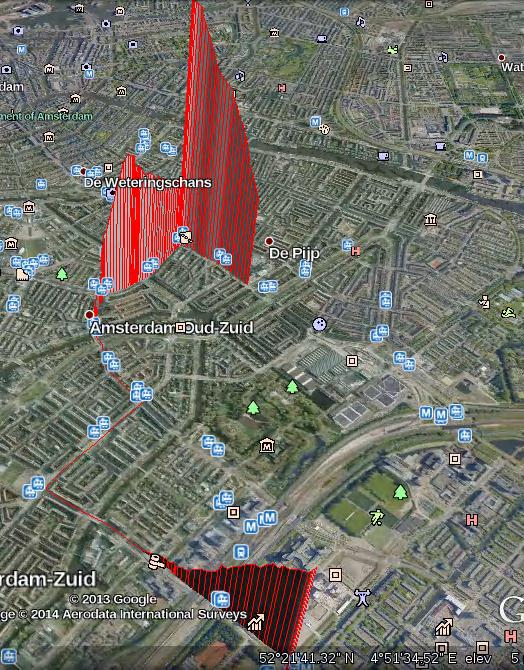 Methane
is not only an energy source, but also a strong greenhouse gas and a safety risk. For environment and safety it is important to reduce methane emissions and leakages, by tracking sources. For this purpose we developed the methane scanner.
Methane
is not only an energy source, but also a strong greenhouse gas and a safety risk. For environment and safety it is important to reduce methane emissions and leakages, by tracking sources. For this purpose we developed the methane scanner.